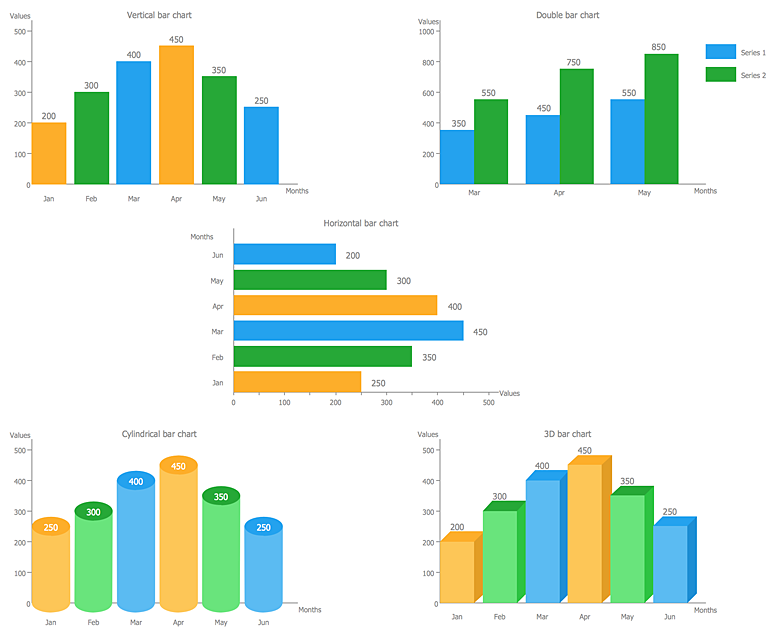
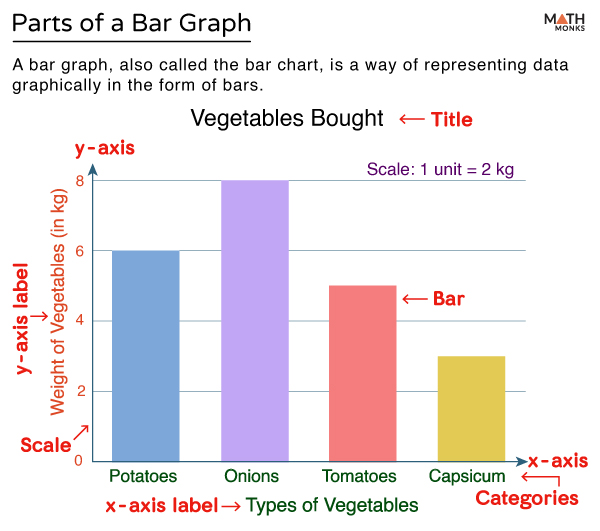
Impressive Info About How To Describe A Bar Graph In Statistics Tableau Axis Label On Bottom

It can be used to display counts (i.e., frequencies) of the categories of a nominal or ordinal variable, as well as illustrating the mean score of a continuous variable for the categories of a nominal or ordinal variable.
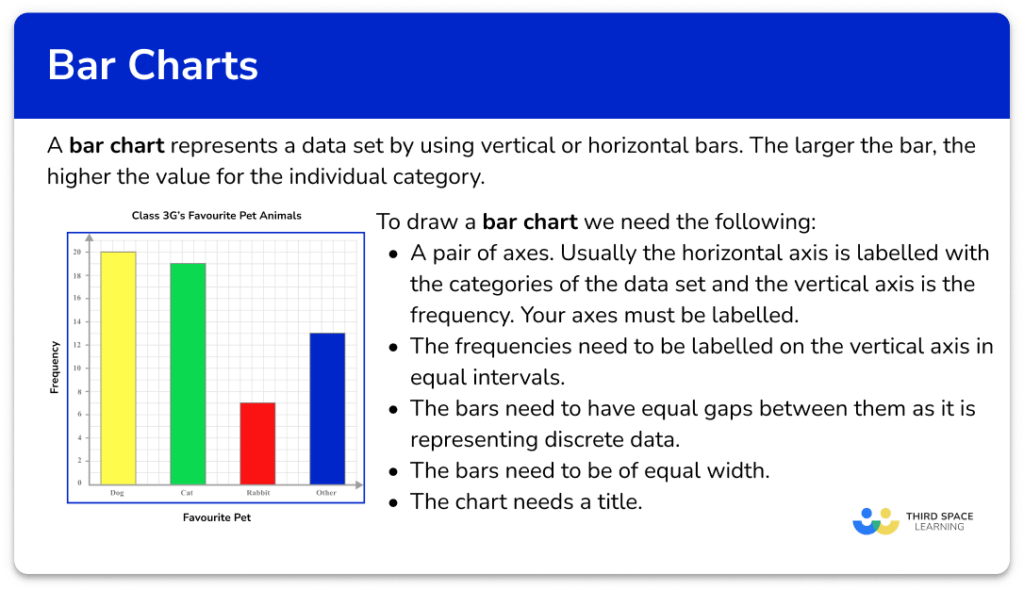
How to describe a bar graph in statistics. Bar charts are also known as bar graphs. A bar graph is used to compare the frequency of a category or characteristic with that of another category or characteristic. A simple bar chart is helpful in graphically describing (visualizing) your data.
The importance of using precise language and statistical terminology when discussing bar graph data. How are bar charts used? The mean, mode, median and range.
Bar charts help you understand the levels of your variable and can be used to check for errors. Let us assume that rob has taken a survey of his classmates to find which kind of sports they prefer and noted the result in the form of a table. Bar graphs and histograms are different things.
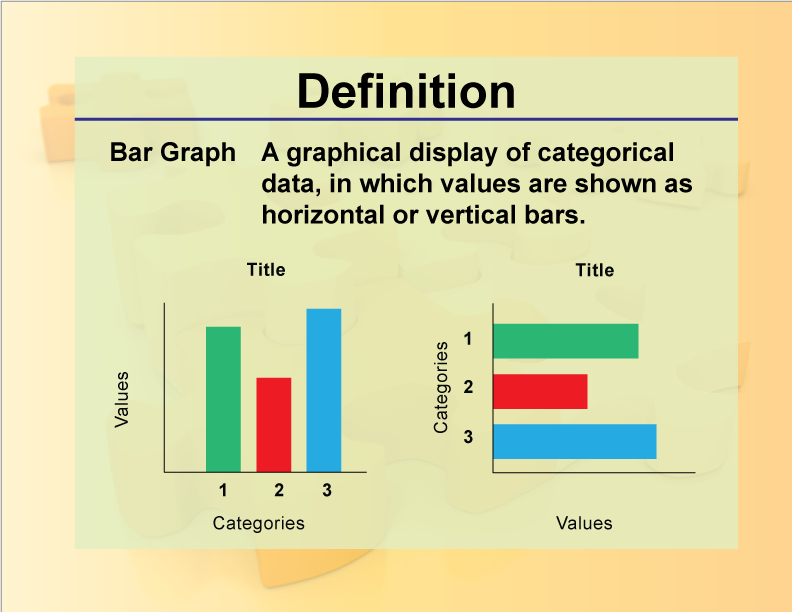
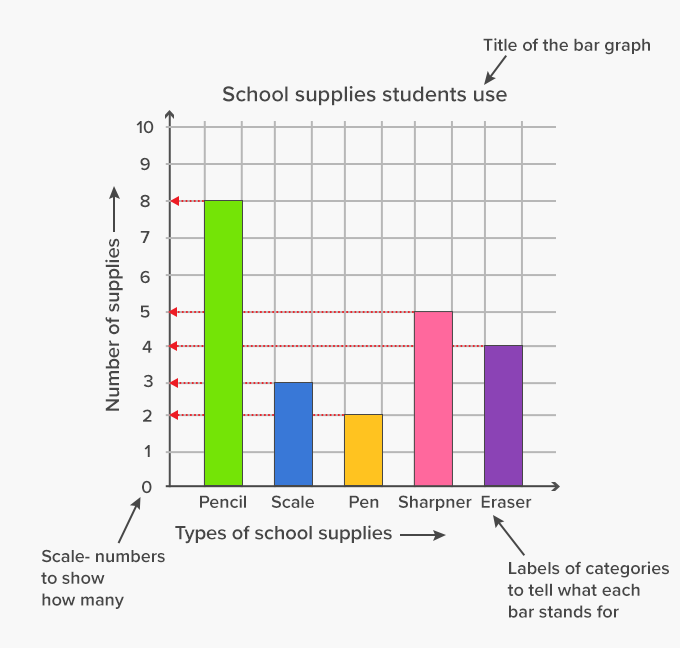
Bar graphs transform the data into separate bars or columns. Bar graphs are the pictorial representation of data (generally grouped), in the form of vertical or horizontal rectangular bars, where the length of bars are proportional to the measure of data. In a bar graph, the length of the bar for each category is proportional to the number or percent of individuals in each category.
A bar chart is a graph with rectangular bars. Strategies for effectively describing the data shown in bar graphs, focusing on clarity, accuracy, and relevance. A bar graph breaks categorical data down by group, and represents these amounts by using bars of different lengths.
Tips for interpreting bar charts, including common pitfalls to avoid and how to draw insights from visual data. It shows the frequency of values in the data. Levels are plotted on one chart axis, and values are plotted on the other axis.
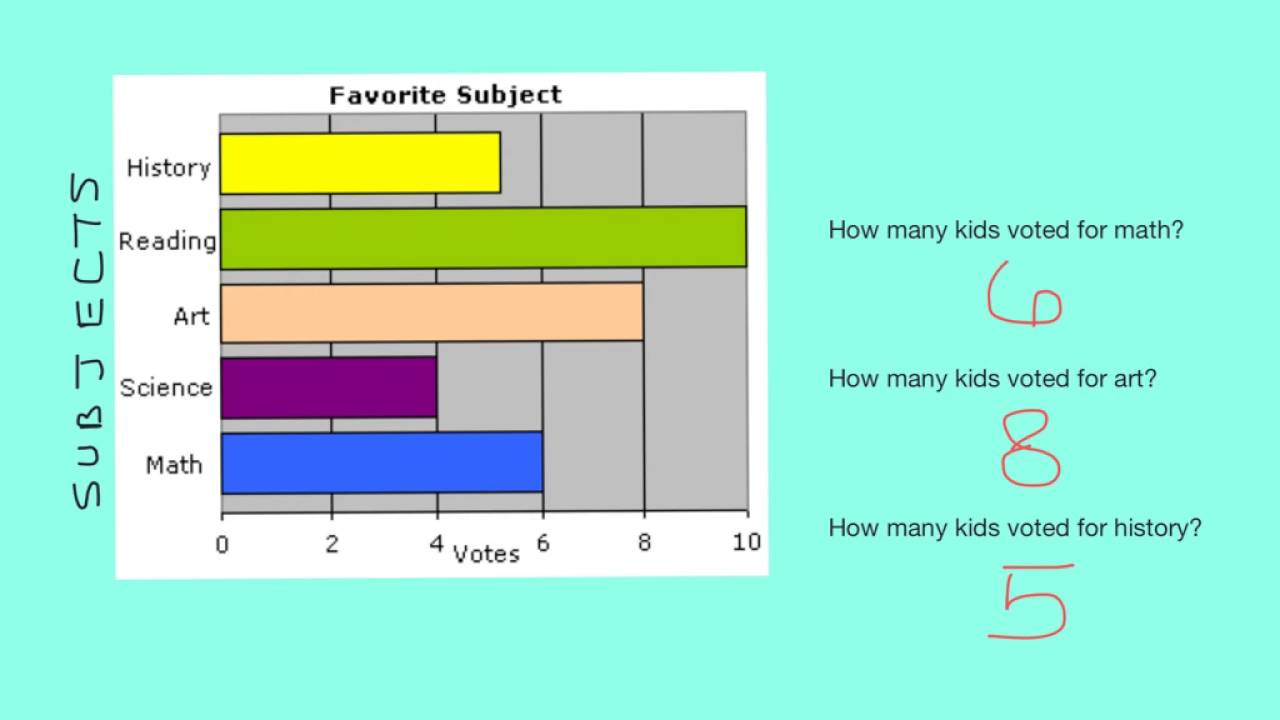
This allows you to compare statistical data between different groups over time. Bars may be vertical or horizontal. Bar charts are used for nominal or categorical data.
The latter associates the bars with intervals of numbers and represents frequency (or probability) by means of area rather than length. Bar charts highlight differences between categories or other discrete data. It also shows the percentage change from the previous year.
These graphs consist of bars or columns of varying heights, which can be horizontal or vertical. The chart shows the sales revenue of a selection of home video entertainment formats in the usa in 2017. Bar graphs are used show the distribution of qualitative (categorical) data.
Purposeful manipulation is fraud and unethical at the worst, but even. Steps to interpret bar graphs. It gives you a general idea of trends in your data including: