Marvelous Info About What Is The Simple Smoothing Method Bar Chart Axis

The stationary represents that the statistical features of a time series don’t change over time.
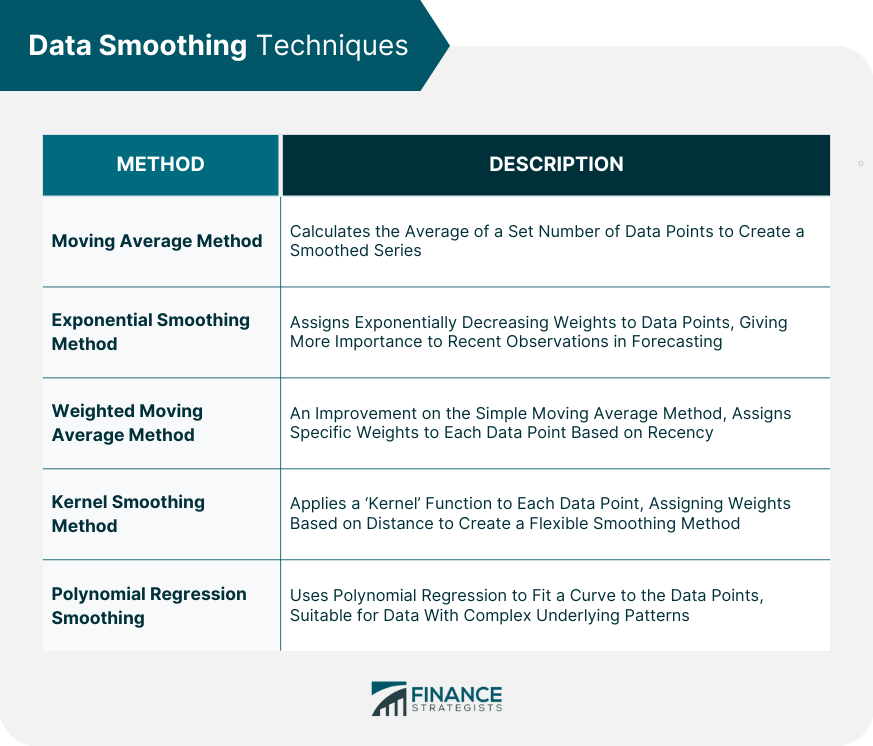
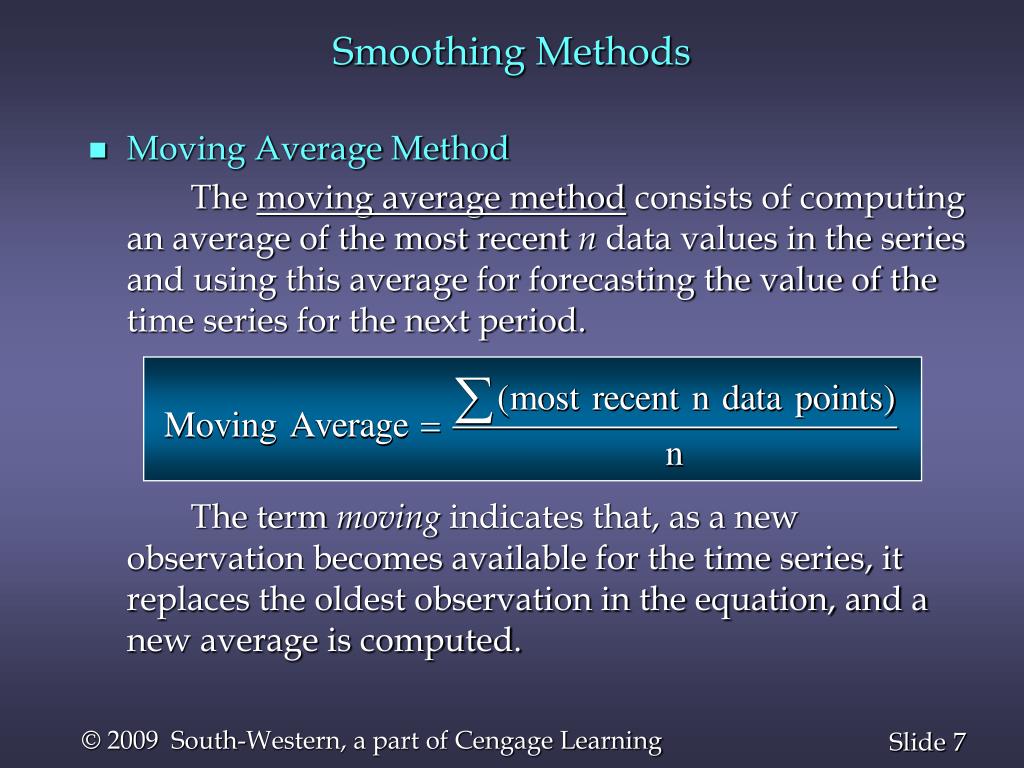
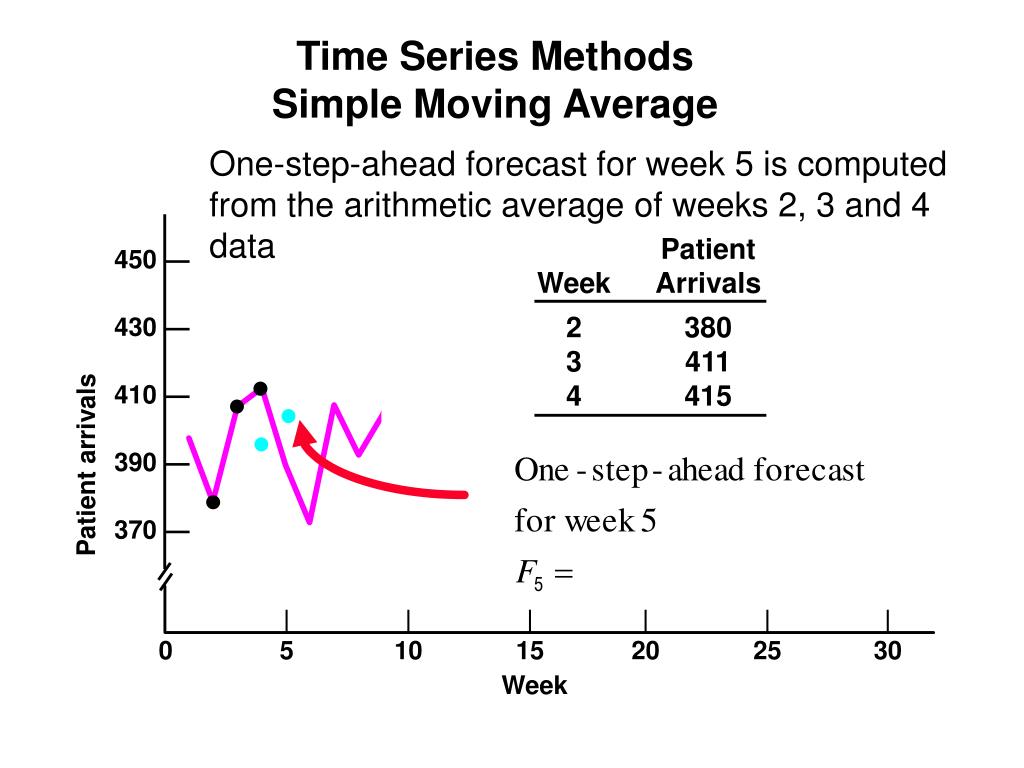
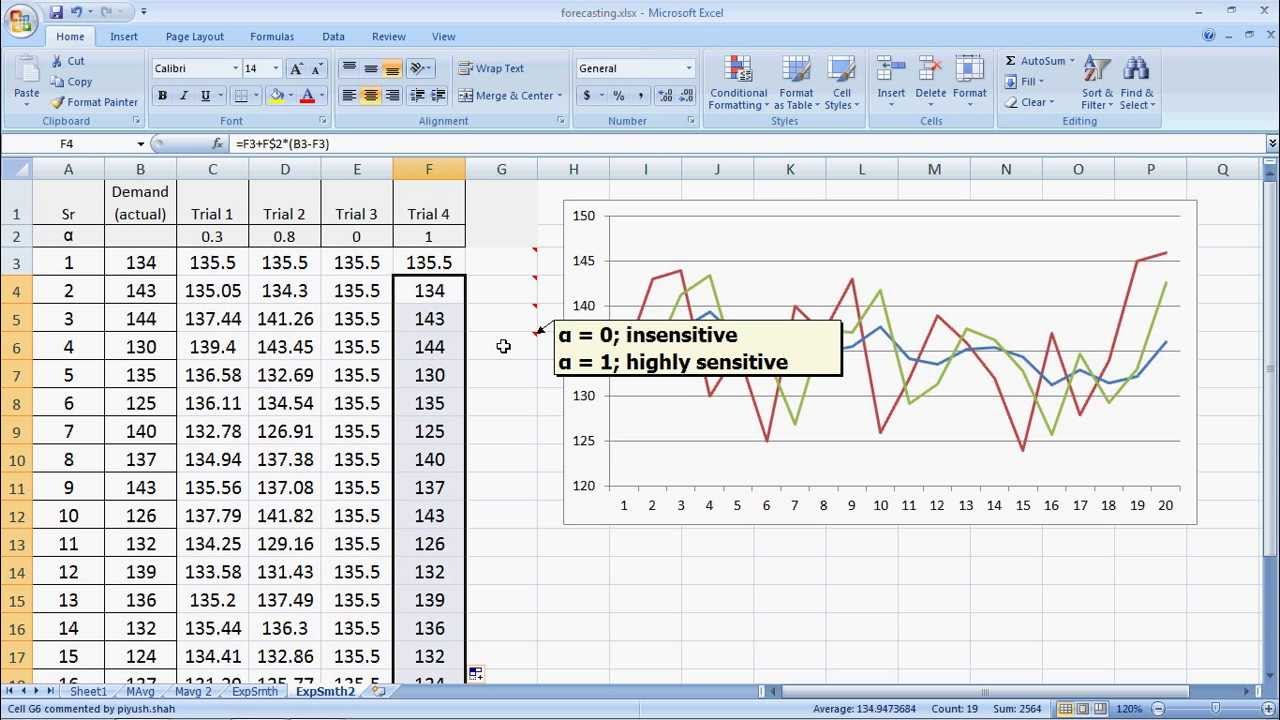
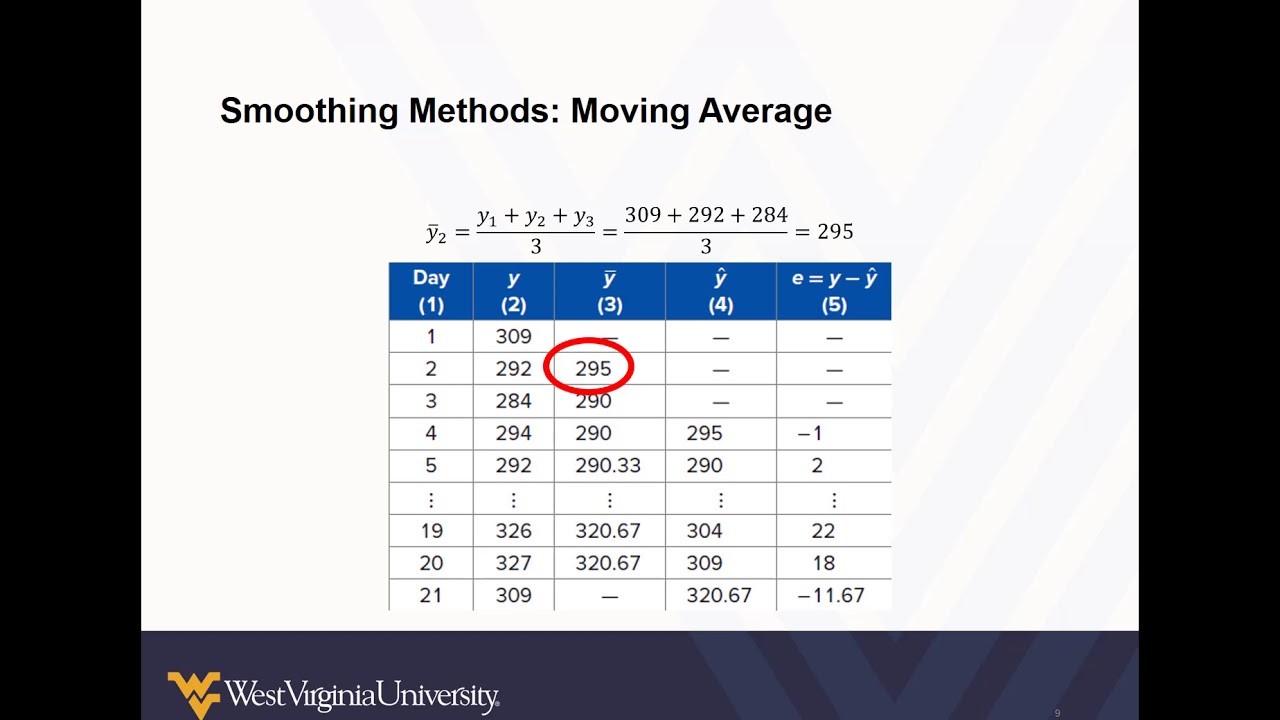
What is the simple smoothing method. Following this, the best value for α is the one that results in the smallest mean squared error (mse). It reduces the noise to emphasize the signal that can contain trends and cycles. This method replaces each point in the signal with the average of m adjacent points, where m is a positive integer called the smooth width.
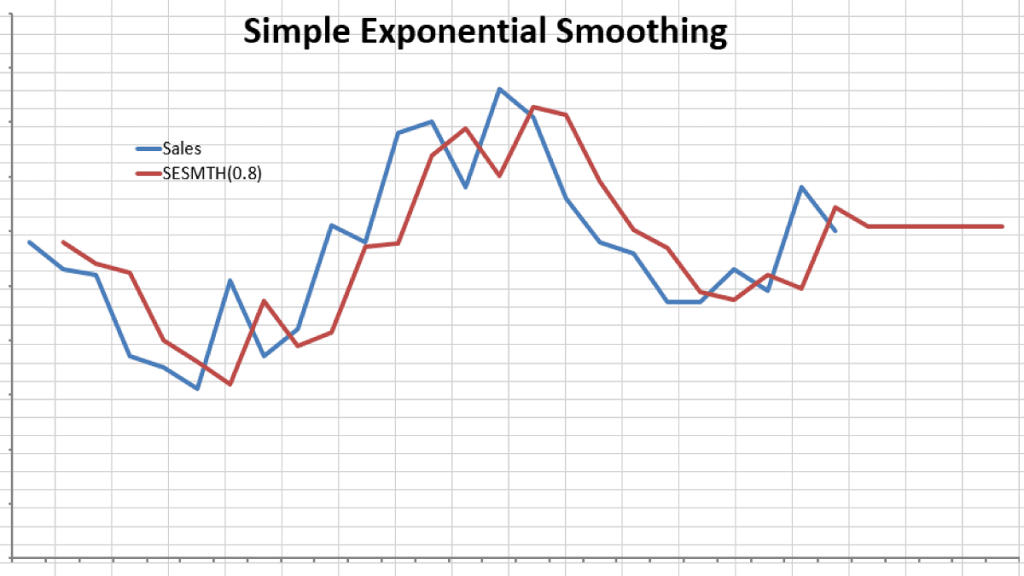
Simple exponential smoothing is a time series forecasting method that assigns exponentially decreasing weights to past observations. We can say the time series is stationary if the average, variance. Generally smooth out the irregular roughness to see a clearer signal.
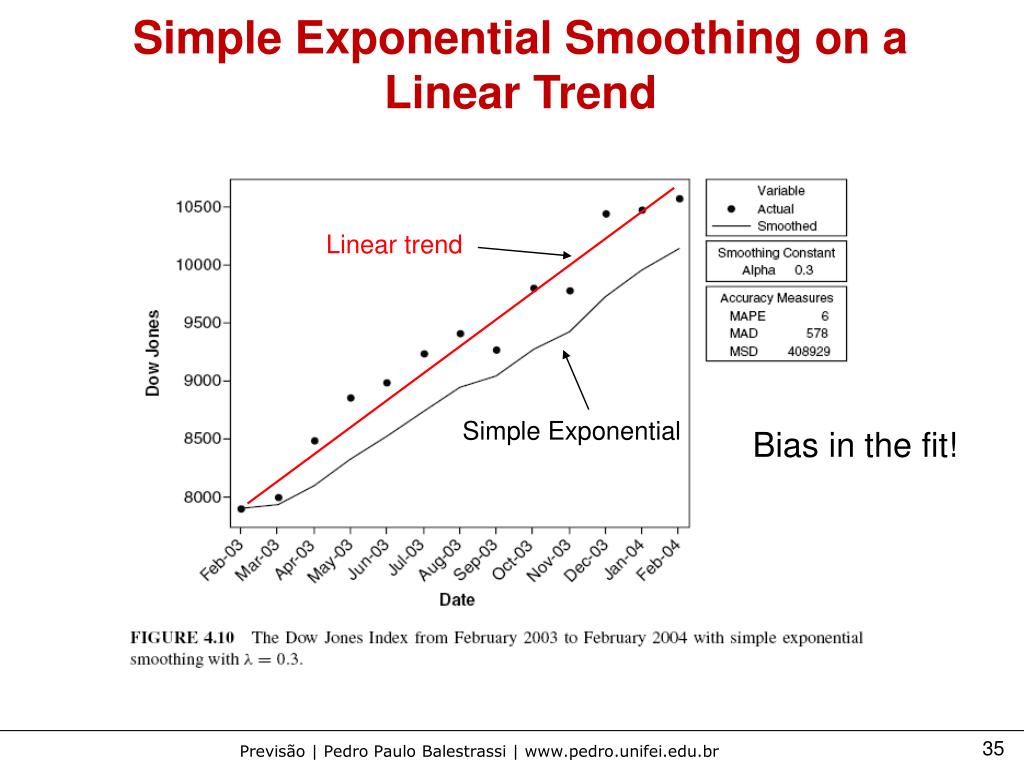
This method is suitable for forecasting data with no clear trend or seasonal pattern. It assumes that the future values of the time series depend solely on the. Simple exponential smoothing is a simple — yet powerful — method to forecast a time series.
For example, the data in figure 7.1 do not display any clear trending behaviour or any seasonality. Whereas in the simple moving average the past observations are weighted equally, exponential functions are used to assign exponentially decreasing weights over time. For example, the data in figure 8.1 do not display any clear trending behaviour or any seasonality.
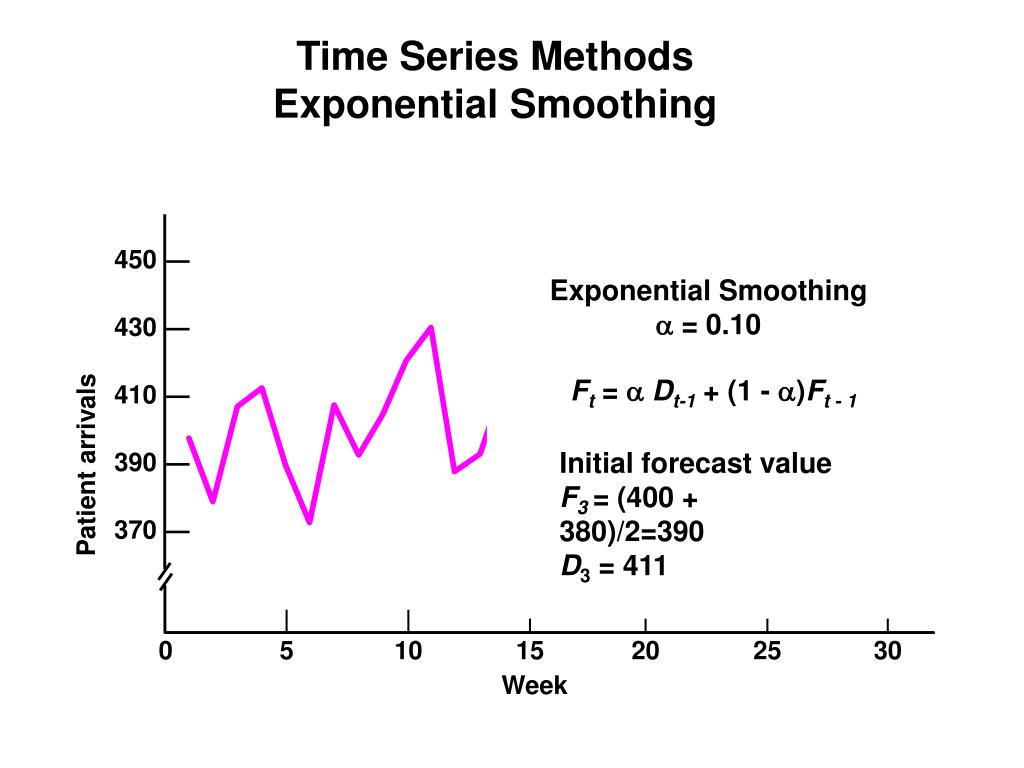
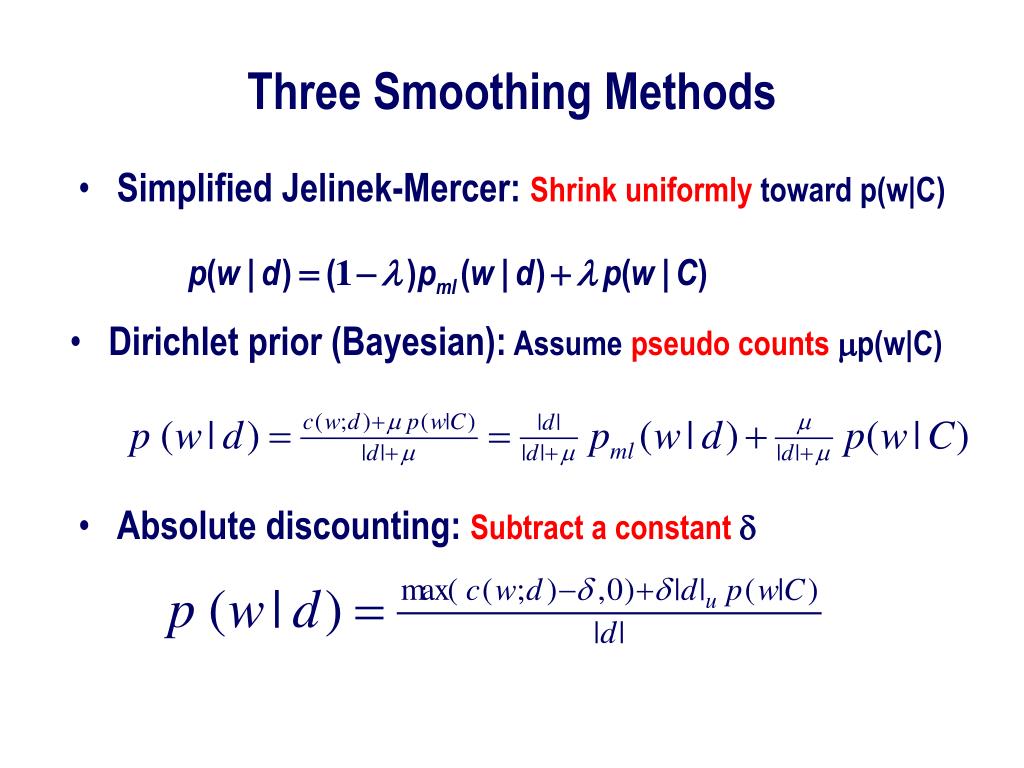
Note that r < t, but r does not have to equal t − 1. In particular, for some α. Y ^ t = α ( y t + ∑ i = 1 r ( 1 − α) i y t − i), where y ^ t is the forecasted value of the series at time t and α is the smoothing constant.
What is simple exponential smoothing? Single exponential smoothing smoothes the data when no trend or seasonal components are present. Smoothing is the process of removing random variations that appear as coarseness in a plot of raw time series data.
The equation for this method is: Let’s see how it works. This method is suitable for forecasting data with no clear trend or seasonal pattern.
In market analysis, smoothed data. Thus, as observations get older in time, the importance of these values get. For seasonal data, we might smooth out the seasonality so that we can identify the trend.
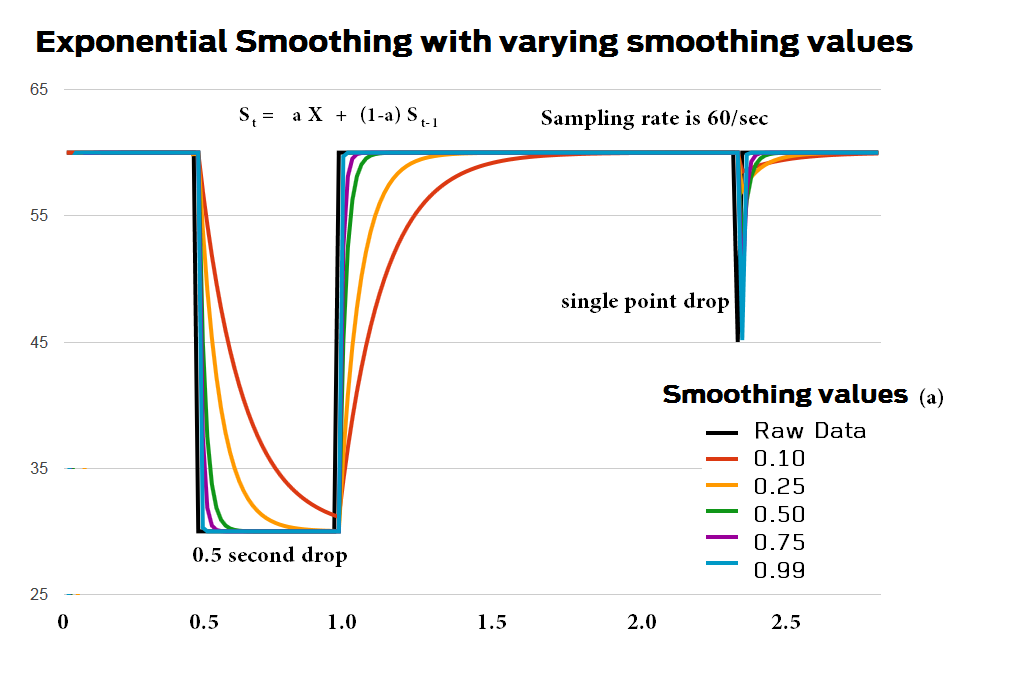
This method produces forecasts that are weighted averages of past observations where the weights of older observations exponentially decrease. This method assigns more weight to recent observations and less to older observations, allowing the forecast to adapt to changing trends in the data. In simple (aka single) exponential smoothing, the forecasted value at time i+1 is based on the value at time i, and the forecasted value at time i (and so indirectly on all the previous time values).
Exponential smoothing is a powerful technique used to forecast univariate time series data. Smoothing is usually done to help us better see patterns, trends for example, in time series. When α is close to zero, smoothing happens more slowly.